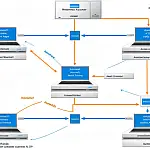
System Lifecycles and SSADMA look at the software development life cycle as defined in SSADM which provides logical data modelling to identif and document the system.
In this article, we will look at the software development life cycle as defined in SSADM. Almost all life cycles will share the same or similar steps, but they may be called something slightly different and have different processes attached to them.
Systems Analysis is a huge topic. This tutorial only provides a brief introduction to the topics involved.
The aim of SSADM is to provide logical data modelling to identify, model and document the data requirements of the system being designed. The data is split into entities and relationships. Data flow modelling documents how data moves through a system and examines processes, entities, data flow and data stores. SSADM also provides tools for entity behaviour modelling.
The SSADM life cycle is a waterfall model, i.e. one stage flows onto the next from the top to the bottom. The life cycle can also be used as an iterative loop model where the final product spawns the next phase in an ongoing system.
There are 5 stages to the SSADM system life cycle that follow the system from the initial idea to the completion of system design.

Feasibility Study
The first phase of SSADM (Stage 1) is the feasibility study in which a team is formed and decides if the project is technically feasible, whether it can be financially and socially acceptable and if the new system will be accepted by the client.
Stage 0. Feasibility Study
SSADM provides detailed instructions on the steps and stages involved.
Requirements Analysis
In this second phase, the existing system is examined in detail to determine the requirements of the new system. This phase is split into two modules.
Stage 1. Investigation of Current System
This stage involved detailed investigation and analysis involving processes and data flow. The system is modelled in a variety of Data Flow Diagrams and Entity models.
Stage 2. Business System Options
Based on the data from the previous stage, various business and technical solutions options are analysed and evaluated with one being selected.
Requirements Specification
3. Definition of Requirements
Using the requirements delivered in Stage 1 and working within the selected business option delivered in Stage 2, a full logical specification is developed as to what the new system must do.
Logical System Specification
Stage 4. Technical System Options
In this stage, various technical options specifying the development and implementation environments are produced, and one is selected.
Stage 5. Logical Design
This stage defines how data is processed by the system and describes user interactions. The specification does not say how the system will be implemented but rather describes what the system will do.
Physical Design
Stage 6 Physical Design
Physical Design consists of a single stage in which the logical system specification and technical system specification are used to create a physical database design and a set of program specifications.
This is only a brief introduction to the SSADM system life cycle. The subject is so vast that one could spend years at university studying.