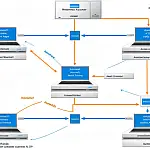
Programming an n-Tier Architecture Design Patternn-Tier Architecture provides a pattern which developers can create reusable applications by separating database from logic and presentation.
In software engineering, multi-tier architecture (often referred to as n-tier architecture) or multilayered architecture is a client's server architecture in which presentation, application processing, and data management functions are physically and logically separated. It allows for a web presentation layer to run on a web server, whilst the business logic and database could be on a different layer, even a different network behind a firewall.
N-tier application architecture provides a model by which developers can create flexible and reusable applications. By segregating an application into tiers, developers acquire the option of modifying or adding a specific layer, instead of reworking the entire application. A three-tier architecture is typically composed of a presentation tier, a domain logic tier, and a data storage tier.

Presentation Layer - n-Tier Architecture
At the top of the diagram, we can see various application types. This is the presentation tier, and it is the responsibility of these applications to only perform the functions to gather and display information. If they are required to perform calculations, store or retrieve data then they must interact with another layer, the business logic layer.
Business Logic - n-Tier Architecture
The business logic is usually a separate assembly or web service which provides a common place for any logic to be performed. This includes calculations, data retrieval and data storage. If this tier requires storing or retrieving data then it, in turn, calls on the data access tier.
Data Access Tier - n-Tier Architecture
The data access tier is only concerned with storing and retrieving data from a data source. At the bottom of the diagram, we can see various data sources - XML, SQL and JSON in this example, however, these can be any source of data. The data access tier is used to query these data sources and return the results to the business logic tier.
Business Objects and Data Transit Objects (DTO)
Business Objects and Data Transit Objects (DTO's) are used to transport data between the layers. DTO's are usually used when transporting data from the Data Access layer, which will map a Data Entity object specific to the database (e.g. an Entity Framework) to a common object shared between the business logic and any other data access layers. The business logic layer will perform any business rules and present a business object to the presentation layer. The business objects are common to all presentation layers.
n-Tier Architecture
Using this architecture, the presentation tier is not concerned with how to retrieve data or the data entities which means that upgrades or extensions to the presentation can be performed quickly. It also means that multiple applications (website, mobile applications, desktop applications, web services and so on) can use the same business logic and data access without duplication of code, resulting in consistent results across applications.
Another advantage of n-Tier Architecture is that separate teams can work on each tier once a common interface is agreed upon. This allows web developers to develop web applications, database application developers to develop data access, Windows Forms developers to develop applications and so on.